lumbar vertical compression test|test for lumbar facet pain : wholesaling Lumbar Assessment - VCT - Vertical Compression Test. Developed by Gregg and Vicky Johnson of the Institute of Physical Art. The way I demonstrate this test is not how . WEBCentro de Previsão de Tempo e Estudos Climáticos. Portais . Tempo Clima Previsão Numérica Satélite Ondas Dados Observacionais Instrumentação Bacias Qualidade do Ar Pós Graduação. Sobre . Sobre o CPTEC Perguntas Frequentes Ouvidoria Links Indicados Biblioteca. Produtos .
{plog:ftitle_list}
r/AlyxStarXX: This is for the fans of Alyx Star
The Vertical Compression Test (VCT) may be used to objectively assess spinal stability and may accurately screen for individuals with postural instability. 1 This test assesses the spine’s. Lumbar Assessment - VCT - Vertical Compression Test. Developed by Gregg and Vicky Johnson of the Institute of Physical Art. The way I demonstrate this test is not how . Patients with a T-score of −2.5 or lower at the femoral neck, total hip, or lumbar spine; a T-score of −1 to −2.4 at the femoral neck or lumbar spine; and a 10-year probability of hip .Spinal cord compression can occur anywhere from your neck (cervical spine) down to your lower back (very top of lumbar spine). Symptoms include numbness, pain, weakness, and loss .
Compression fractures are usually caused by an axial load on the anterior part of the vertebrae. Due to this vertical force, this specific part of the vertebrae will lose height and will become wedge-shaped. Lhermitte sign. a positive test is specific, but not sensitive, for cervical spinal cord compression and myelopathy. test is positive when cervical flexion or extension leads to shock-like sensation radiating down the spinal .The Straight Leg Raise (SLR) test is commonly used to identify disc pathology or nerve root irritation, as it mechanically stresses lumbosacral nerve roots. It also has specific importance .
Vertical Compression Test. The Vertical Compression Test is a test of force transfer. During this test practitioners apply force through the shoulders with the client in standing and observe for two things: ‘buckling’ . 19 Altmetric. Metrics. Abstract. Background. Only low-quality evidence is currently available to support the effectiveness of different traction modalities in the treatment of lumbar radiculopathy (LR). Yet, traction is still . Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures are very common fragility fractures of the spine that affect up to 50% of people over 80 years old. Diagnosis can be made with lateral radiographs. Determining the .
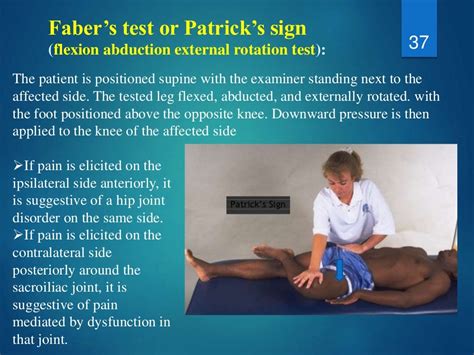
test for lumbar facet pain
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Spurling's test (also known as Maximal Cervical Compression Test and Foraminal Compression Test) is used during a musculoskeletal assessment of the cervical spine when looking for cervical nerve root compression causing Cervical Radiculopathy.. Technique [edit | edit source]. There are different ways described in the literature to perform . It is our mission to challenge sports and orthopedic physical therapists to become clinical experts by providing residency level education.Follow us! EMAIL:. Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) of the spinal column occur secondary to an axial/compressive (and to a lesser extent, flexion) load with resultant biomechanical failure of the bone resulting in a fracture. VCFs by definition compromise the anterior column of the spine, thereby resulting in compromise to the anterior half of the vertebral body (VB) and the anterior .
A herniated disc in the spine is a condition during which a nucleus pulposus is displaced from intervertebral space. It is a common cause of back pain. The patient's who experience pain related to a herniated disc often remember an inciting event that caused their pain. Unlike mechanical back pain, herniated disc pain is often burning or stinging, and may radiate into the . due to the vertical anatomy of lumbar nerve root, a paracentral and foraminal disc herniation will affect different nerve roots. . foraminal compression test that is specific, but not sensitive, in diagnosing acute radiculopathy. performed by rotating head toward the affected side, extending the neck, and then applying and axial load .
starter cable voltage drop test
Most people with back pain consult their primary health care provider first. The doctor will begin with a thorough medical history and physical exam. If a doctor believes a spinal compression fracture may be present, the following tests may be ordered:X-rays are usually the first tests ordered; they can show which bones have fractured. Lumbar Orthopaedic Tests Palpation Spinous Processes Descriptive Anatomy The five lumbar spinous processes are large and easily palpable with the spinal column in the flexed position (Fig. 10-1). The fifth lumbar vertebra is the lowest movable segment. In 5% of the population, the fifth lumbar vertebra is congenitally fused to the sacrum, a condition called. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday Ticket Press Copyright . Low back pain (LBP) is a common musculoskeletal disorder [].Most LBP are non-specific, and only 3–5% of the general population is affected by lumbar radiculopathy (LR) [], that is a pain syndrome caused by compression and/or irritation of lumbar nerve roots [].LR is a common reason for physician consultations and imaging referrals []; typical symptoms are .
The thinning bones can collapse during normal activity, leading to a spinal fracture. These compression fractures can cause a great deal of pain and can permanently alter the shape and strength of the spine. . the doctor will test for tenderness and sensitivity near specific vertebrae along the spine. Based on the patient's history and .Due to this vertical force, this specific part of the vertebrae will lose height and will become wedge-shaped. . SCT is a sensitive diagnostic test for the identification of spinal fractures. A more recent study by Ang et al . ↑ Andrew L Sherman et al. “Lumbar Compression Fracture” May 23, 2016; ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 American Academy of .Chronic compression develops over months to years. It is commonly caused by. Bony protrusions into the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spinal canal (eg, due to osteophytes or spondylosis, especially when the spinal canal is narrow, as occurs in spinal stenosis) Compression can be aggravated by a herniated disk and hypertrophy of the ligamentum .
The lumbar compression forces sustained in the reclined seat back positions were reduced effectively by the active seat track load r from 6 kN limite to the 4 kN levels observed for upright occupants.
Discectomy: This procedure involves removing a portion of a disk to relieve pressure off nearby roots.; Corpectomy: A corpectomy involves removing part or all the vertebral body to decompress the spinal cord and nerves. This . Cervical myelopathy is compression on your spinal cord in your neck. The most common type is cervical spondylotic myelopathy. . They may also test your balance, reflexes and dexterity, and observe you walking (if .Unlike many other conditions, diagnosing a vertebral compression fracture is not as straightforward as one would think. For example: When an elderly person complains of back pain, it is often assumed to be just general back pain, . Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the nerve roots are compressed by a number of pathologic factors, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness. The upper neck (cervical) and lower back (lumbar) areas most frequently are affected, although the thoracic spine also can be compressed most frequently by a disk herniation. Three different .
Introduction [edit | edit source]. Lumbar radiculopathy is usually caused by compression of a lumbar nerve root, resulting in symptoms which radiate down the legs. It causes at least one of the following: decreased strength in the associated myotome, altered sensation in the dermatome or decreased reflexes. While pain is not part of this definition, people with lumbar . Spinal cord compression can result from a myriad of both atraumatic and traumatic causes. The spinal column, comprised of numerous soft tissue and bony structures, is built to provide the body’s structural support and protect the spinal cord and exiting nerve roots. The encased spinal cord depends upon this stability. However, it is simultaneously vulnerable .
Posterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF, TLIF) are well-established procedures for spinal fusion. However, little is known about load sharing between cage, dorsal construct, and biological tissue within the instrumented lumbar spine. . Biomechanical test setup for application of a vertical compression force (C). The .Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a labral tear or acromioclavicular lesion. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is instructed to place the shoulder into 90 degrees of flexion and 10 degrees of adduction. Next, the arm is actively internally rotated so the thumb is pointing downward. The instructor then applies a inferior directed force (into .
sciatica symptoms result from combined mechanical compression and associated inflammation. not all patients with mechanical compression develop symptoms . because of vertical anatomy of lumbar nerve root a paracentral and foraminal disc will affect different nerve roots . femoral nerve stretch test (Wasserman sign) tension sign for L2 and .
K.-D. Bouzakis et al.: Loading simulation of lumbar spine vertebrae 155 A significant condition in nanoindentation evaluation procedures is the precise knowledge of the indenter tip
The spine and the body function within a cone of equilibrium with the focus of maintaining sagittal and coronal alignment with minimum energy expenditure. This happens with a harmonious relationship involving cervical lordosis, thoracic kyphosis, lumbar lordosis, and pelvic anatomy. The purpose is mostly to maintain a mechanical balance in the sagittal plane and . The Lumbar Quadrant test is designed to detect the involvement of the lumbar zygapophyseal joints. This test is also referred to as the Quadrant test, the Extension-Rotation Test, and the Kemp’s Test. To perform this test, ask the patient to stand with their arms crossed in front of the chest.cancellous bone region and adjustable stiffness in vertical and horizontal directions. Experimental setup of the vertebral body compression test The experimental setup used for the vertebrae compres-sion test is shown in the left part of Figure 1. The compres-sion was performed between two rigid steel plates. Through
positive quadrant test lumbar spine
starter cables voltage drop test
starter control circuit voltage drop test
WEB16 de jul. de 2021 · Dicas de como trabalhar a Letra Cursiva. Neste site você irá relacionar a letra bastão e cursivaLink para o jogo: .
lumbar vertical compression test|test for lumbar facet pain